SERVICES
- Allergy Screening
- Chemical Peels
- Dermapen
- Facial Skin Analysis
- FreshEyes
- Hyperhidrosis (Excessive Sweating)
- Hair Loss Treatment
- Laser Clinic
- Liquid Facelift
- Keloid Treatments
- Medical Facials
- Medical Treatments
- Mole Mapping
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
- Skincare Advice
- Pigmentation Treatment
- Surgical Procedures
- Ultraviolet Phototherapy
USEFUL LINKS
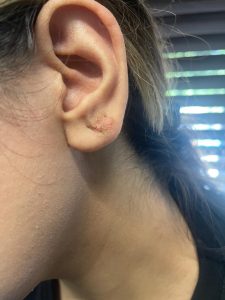
Keloid treatments
Keloids are overgrowths of scar tissue that extend beyond the original wound boundary and
can be itchy, painful, or cosmetically distressing. Management is often challenging because recurrence is common, and no single therapy works for everyone. Usually, treatment involves combination approaches.
Treatment options
- Intralesional corticosteroids (e.g., triamcinolone acetonide)
- Reduces fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis.
- Given every 4–6 weeks.
- Side effects: skin thinning, hypopigmentation.
- Intralesional 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)
- Often combined with corticosteroids.
- Improves response rates and reduces recurrence.
- Intralesional bleomycin or interferon
- Used in resistant cases.
Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen spray or contact)
- Effective for small keloids.
Surgical excision
- High recurrence risk if done alone.
- Best combined with adjuvant therapy (steroid injections, radiation, or pressure therapy)
Before and After

Patient Testimonials
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. From my first visit with Dr Jhetam I knew I would go back. He is compassionate , friendly and has an interaction which made you feel comfortable. This is very important in any doctor because our relationship with our doctor is very intimate.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr Jhetman is truly one of a kind. Anyone who is fortunate enough to be in his care can so grateful. Academic, informative and reassuring. It’s hard to find a doctor who has this combination of skills these days. He dealt with my Melonoma concerns with swift and professional care. And his staff are equally as competent and caring. I cannot commend Dr Jhetman and his staff enough on true patient care. Thank you!Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I was absolutely satisfied with my experience with Dr Jhetham & his winning team. Keep up the good work.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best skin doctor..Dr Jetham prescribed the best products that have brought so much of a glow to my skin..being a transplant patient and so much happening to my skin just 4 visits to him and my face is back to it's radiance ..I hightly reccomend Dr Jetham ...you won't go wrong..Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr. Imraan Jhetam and his team provided exceptional care, showcasing professionalism and compassion in every interaction. Dr. Jhetam took the time to thoroughly explain everything, addressing each of my concerns with empathy and understanding. My experience with him was truly wonderful, and I highly appreciate his dedication to patient care.Verified by TrustindexTrustindex verified badge is the Universal Symbol of Trust. Only the greatest companies can get the verified badge who has a review score above 4.5, based on customer reviews over the past 12 months. Read more