What is rosacea?
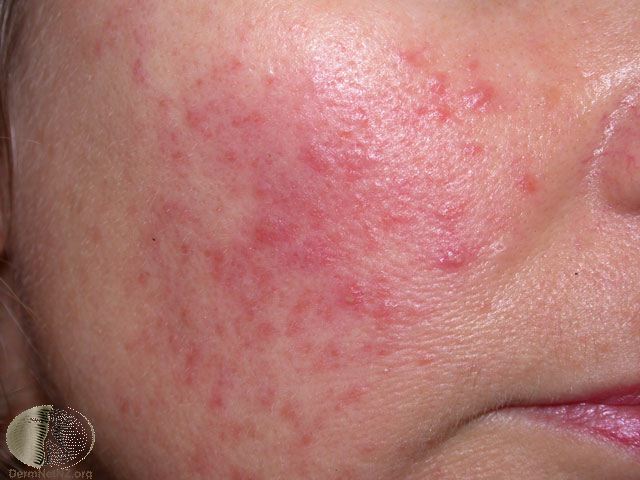 Rosacea is a common rash, found on the central part of the face, usually of a middle-aged person. A tendency to flush easily is followed by persistent redness on the cheeks, chin, forehead and nose, and by crops of small inflamed red bumps and pus spots.
Rosacea is a common rash, found on the central part of the face, usually of a middle-aged person. A tendency to flush easily is followed by persistent redness on the cheeks, chin, forehead and nose, and by crops of small inflamed red bumps and pus spots.
What causes rosacea?
The cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but many think that the defect lies in the blood vessels in the skin of the face, which dilate too easily. Rosacea is more common in women than in men, and in those with a fair skin who flush easily.
Many things seem to make rosacea worse, but probably do not cause it in the first place. They include alcohol, too much exercise, both high and low temperatures, hot spicy foods, stress, and sunlight. Things that stir up one person’s rosacea may well have no effect at all on the rosacea of someone else. The idea that rosacea is due to germs in the skin, or in the bowel, has not been proved. Rosacea is not catching.
Is rosacea hereditary?
Rosacea does seem to run in some families but it is still not clear whether heredity plays a big part in this.
What are the symptoms of rosacea?
The skin of the face feels sensitive, and can burn or sting. Flushing (the face becomes bright red) adds to the embarrassment caused by the rash. Be sure to consult your doctor if you have problems with your eyes (see below).
What does rosacea look like?
Rosacea starts with a tendency to blush and flush easily. After a while, the central areas of the face become a deeper shade of red and end up staying this colour all the time. The area becomes studded with small red bumps (papules) and pus spots, which come and go in crops. Small dilated blood vessels (telangiectasia) appear, looking like thin red streaks. Scarring is seldom a problem.
Other problems with rosacea include the following:
- Rosacea can lead to embarrassment, anxiety, or depression, and a disrupted social life.
- The face may swell (lymphoedema), especially around the eyes.
- The nose may grow big, red and bulbous (rhinophyma) due to the overgrowth of the sebaceous glands. This is more common in men than women.
- Some people with rosacea have eye symptoms (red, itchy, sore eyes and eyelids; a gritty feeling; sensitivity to light). A few patients with rosacea have more serious eye problems, such as rosacea keratitis, that can interfere with vision.
How will rosacea be diagnosed?
Your doctor will recognise rosacea just by looking at your skin. There are no diagnostic laboratory tests. Rosacea differs from acne in that the skin is not extra-greasy; blackheads and scarring are not features; flushing is common; and there is a background of red skin.
Can rosacea be cured?
No treatment can be guaranteed to switch rosacea off forever. However long-term treatments control symptoms and can clear the spots. Treatment works best if started when rosacea is at an early stage.
How can rosacea be treated?
Rosacea may last for years if not treated. Preparations applied to the skin can sometimes control mild rosacea, or keep rosacea in remission after a course of oral antibiotics. Most people with rosacea, however, need to take antibiotics by mouth from time to time.
Local applications for rosacea:
- Useful preparations include a gel containing metronidazole, and antibiotic preparations containing clindamycin or erythromycin. Don’t give them up too soon: they take time — at least 8 weeks - to have their effect.
- It may be best to avoid treatments designed for acne — some can irritate rosacea.
- Note that preparations containing strong corticosteroids will make rosacea worse in the long run and should be avoided. In the long term they turn the face redder; make the streaky blood vessels (telangiectasia) more obvious; and everything flares up worse than before, when they are stopped (a rebound flare).
Antibiotics for rosacea:
The most commonly used antibiotics, such as oxytetracycline, belong to the tetracycline group. Courses usually last for around 10 weeks. After that, the dose can be dropped, or the treatment can be stopped if the rosacea has cleared. If a tetracycline has not helped after a reasonable trial lasting several months, then another antibiotic, such as erythromycin, can be tried.
Other treatments:
- An eye specialist should manage the more severe types of eye involvement.
- An antidepressant may help depression caused by rosacea.
- A bulbous nose affected by rhinophyma can be reduced surgically.
- Ugly dilated small blood vessels can be destroyed with a laser.
- A beta-blocker tablet may help if flushing is a big problem.
- Isotretinoin tablets are occasionally given for very severe rosacea, but the great risk of taking it during pregnancy must always be kept in mind.
What can I do?
- Protect your skin from the sun by using a sun block on your face every day.
- Do not rub or scrub your face as this can make rosacea worse.
- Consider the lifestyle factors that can stir up rosacea (listed above). Learn which worsen your rosacea and avoid them. A written record of your flare-ups may help here.
- Cosmetics can often cover up rosacea effectively.
- If your eyes are giving problems, do not ignore these - consult your doctor.